What is Robustel Edge2Cloud?
Edge2Cloud (E2C) is a collection of software applications that can run within Robustel’s “RobustOS” operating system to provide IoT Gateway functionality at both a hardware and software level.
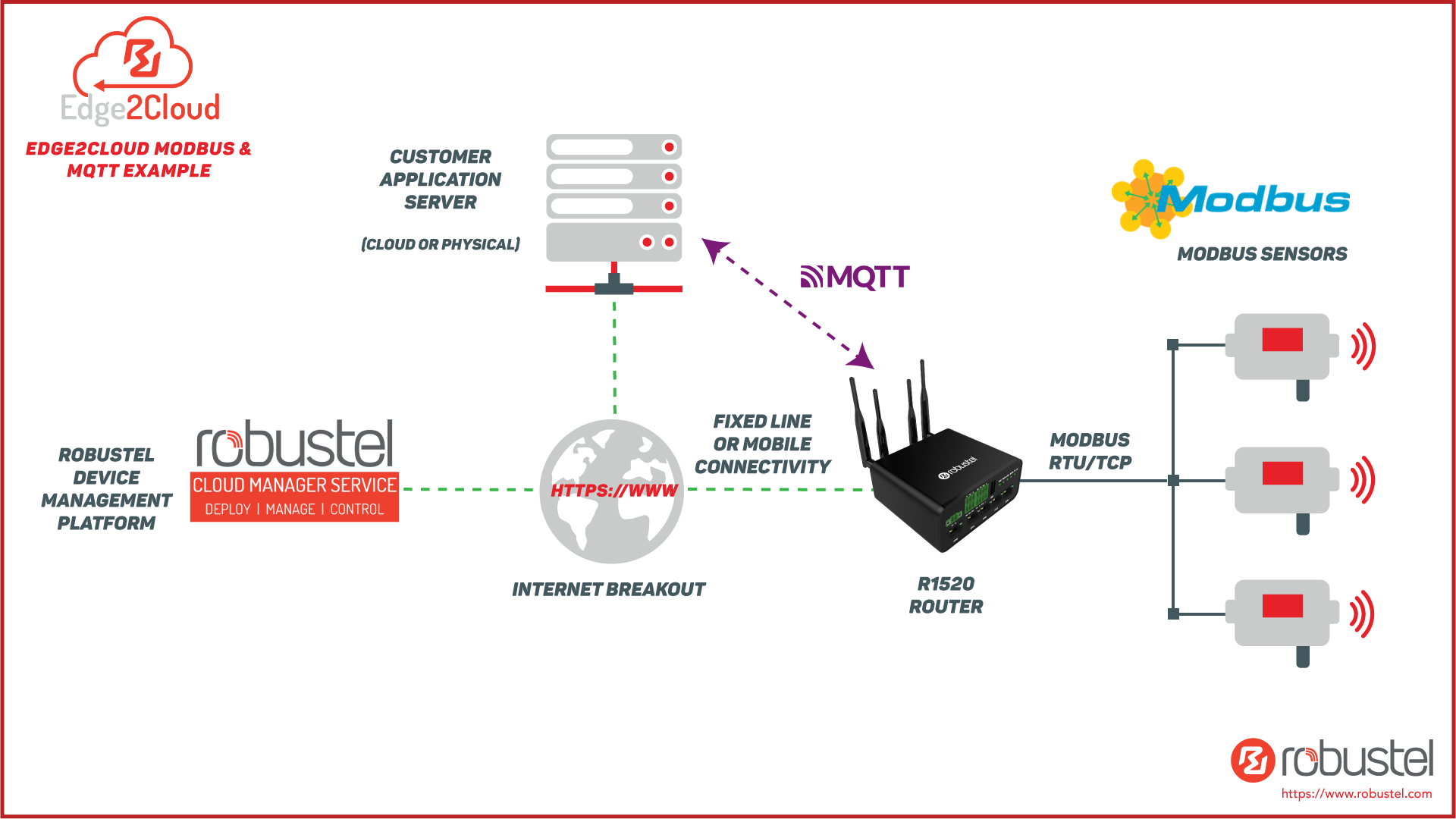
For many years, Robustel have been writing custom applications to help connect legacy industrial protocols (e.g. Modbus) and equipment to application servers in the cloud. E2C is a ‘root and branch’ attempt to formalise that capability. This saves you time and cost when developing new applications.
The most common example of this at the time of writing is the requirement to move Modbus (RTU or TCP) data from the edge to cloud services such as MS Azure and Amazon AWS. E2C provides a framework to make these requirements easy to implement.
Features & Benefits of Edge2Cloud
for IoT Applications
Connect Industrial devices
(Modbus/OPC UA/Siemens S7 etc.) to the Cloud with zero edge software effort
This simple, low-cost solution can replace an additional Embedded PC and reduce panel size leading to significant cost-savings
When used in R1520G gateway, the customer gets a globally certified solution in a single box – no need for regional variants
E2C runs in Robustel’s R152X low-cost
“Lite Industrial” range, providing a cost-effective solution for high-volume deployments
E2C allows a single Gateway to capture and concentrate multiple different industrial protocols over a single connection to the cloud
E2C runs within the Linux-based “RobustOS” – an environment providing excellent tech support and customisation capability
How does Edge2Cloud work?
E2C comprises 3 layers of software that run on a Robustel Gateway.
The diagram below highlights the fundamental structure of E2C.
The “Southbound” app is responsible for interfacing with industrial protocols/sensors over RS232, RS485, Bluetooth, Ethernet, etc.
The “Northbound” app is responsible for transmitting data to Cloud services/protocols as required by the customer application.
In between Northbound and Southbound app is the “Broker”, which decouples the two interfaces. It provides a generalised “any to any” transmission path for disparate types of data and destinations.
The Broker in this instance should not be confused with a typical MQTT Broker used elsewhere in the solution architecture.